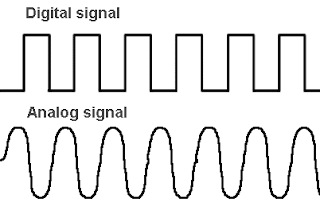
DIGITAL SIGNAL
A digital signal is a physical signal that is a representation of a sequence of discrete values (a quantified discrete-time signal), for example of arbitrary bit stream, or of a digitized (sampled and analog-to-digital converted) analog signal. The term digital signal can refer to a continuous-time waveform signal used in any form of digital communication or a pulse train signal that switches between a discrete number of voltage levels or levels of light intensity, also known as a a coded signal, for example a signal found in digital electronics or in serial communications using digital baseband transmission in, or a pulse code modulation (PCM) representation of a digitized analog signal.
A digital signal waveform: (1) low level, (2) high level, (3) rising edge, and (4) falling edge.
In computer architecture and other digital systems, a waveform that switches between two voltage levels representing the two states of a Boolean value (0 and 1) is referred to as a digital signal, even though it is an analog voltage waveform, since it is interpreted in terms of only two levels.
The clock signal is a special digital signal that is used to synchronize digital circuits. The image shown can be considered the waveform of a clock signal. Logic changes are triggered either by the rising edge or the falling edge.